In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are under constant pressure to deliver innovative products and services at an ever-increasing pace. To thrive in this environment, organizations are turning to DevOps—a methodology that blends people, processes, and products to enable continuous delivery of value to end users. This blog post explores the fundamental aspects of DevOps, its benefits, and the key practices that drive its success.
What is DevOps?#
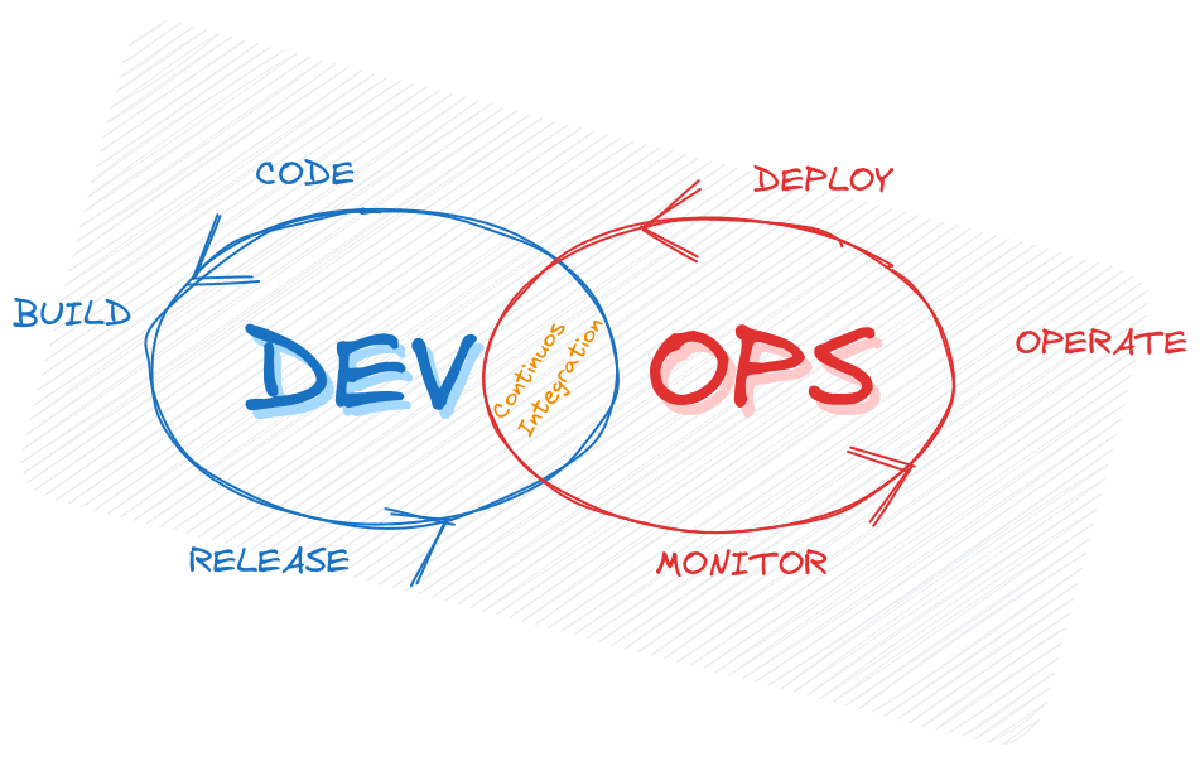
DevOps is a cultural and operational model that emphasizes the collaboration between development and operations teams. As defined by Donovan Brown, a well-known figure in the DevOps community, “DevOps is the union of people, process, and products to enable continuous delivery of value to our end users.” This integration seeks to break down the traditional silos between software development and IT operations, fostering a collaborative environment that enhances efficiency and accelerates delivery.
The Benefits of DevOps#
Adopting DevOps offers several compelling benefits for organizations, including:
- Accelerating Time to Market: By automating processes and improving collaboration, DevOps enables teams to bring products to market faster, ensuring that businesses stay ahead of the competition.
- Adapting to Market Changes: DevOps allows organizations to quickly adapt to market dynamics and competitive pressures by enabling more frequent and reliable updates to applications and services.
- Maintaining System Stability and Reliability: Through continuous monitoring and automated testing, DevOps helps maintain high levels of system stability and reliability, reducing the risk of downtime and ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Improving Mean Time to Recovery: In the event of an issue, DevOps practices enable teams to recover more quickly, minimizing the impact on end users and maintaining trust in the product.
The Application Lifecycle in DevOps#
DevOps influences every phase of the application lifecycle—plan, develop, deliver, and operate. In a true DevOps culture, all roles are involved in each phase to some extent, fostering a holistic approach to software development and operations.
- Plan: Collaborative planning ensures that all stakeholders are aligned on the goals and requirements of the project.
- Develop: Continuous integration and automated testing accelerate development cycles and improve code quality.
- Deliver: Automated deployment processes enable frequent and reliable releases, reducing the time it takes to deliver new features to users.
- Operate: Continuous monitoring and feedback loops allow for proactive maintenance and rapid response to any issues that arise.
The Importance of Culture in DevOps#
While tools and processes are crucial, the foundation of DevOps lies in the culture of the organization. Cultivating a DevOps culture requires significant changes in how teams work and collaborate. Key cultural shifts include:
- Collaboration, Visibility, and Alignment: Breaking down silos and fostering open communication across teams is essential for successful DevOps implementation.
- Shifts in Scope and Accountability: Teams must embrace shared responsibility for the entire lifecycle of the product, from development to operations.
- Shorter Release Cycles: By adopting a mindset of continuous improvement, teams can release updates more frequently and with greater confidence.
- Continuous Learning: A commitment to ongoing education and skill development ensures that teams stay current with best practices and emerging technologies.
Core DevOps Practices#
To bring the DevOps culture to life, organizations implement various practices throughout the application lifecycle. These practices include:
- Version Control: Managing changes to code and configuration files in a version control system is fundamental to DevOps, enabling teams to track changes and collaborate effectively.
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Automating the integration and delivery process ensures that code is always in a deployable state, reducing the risk of errors and accelerating release cycles.
- Agile Software Development: Agile methodologies complement DevOps by promoting iterative development, flexible planning, and continuous feedback.
- Infrastructure as Code: Managing infrastructure through code allows for consistent and repeatable deployments, enhancing scalability and reliability.
- Configuration Management: Automated configuration management tools ensure that systems are configured correctly and consistently across environments.
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitoring applications and infrastructure in real-time enables teams to detect and resolve issues before they impact end users.
Conclusion#
DevOps is more than just a set of tools or practices—it’s a cultural shift that requires organizations to rethink how they build, deploy, and maintain software. By fostering collaboration, automating processes, and embracing continuous learning, organizations can leverage DevOps to bring better products to end users faster. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, DevOps will remain a critical driver of innovation and competitive advantage.
Whether you’re just beginning your DevOps journey or looking to refine your existing practices, remember that success lies in the union of people, processes, and products working together to deliver continuous value.